A novel strategy for JEV to escape the host innate immune response is revealed
Date:05-04-2017 | 【Print】 【close】
JEV is the major cause of viral encephalitis in South and Southeast Asia with high mortality. However, the molecular mechanisms contributing to the severe pathogenesis are poorly understood. The ability of JEV to counteract the host innate immune response may be one of the potential mechanisms responsible for JEV virulence.
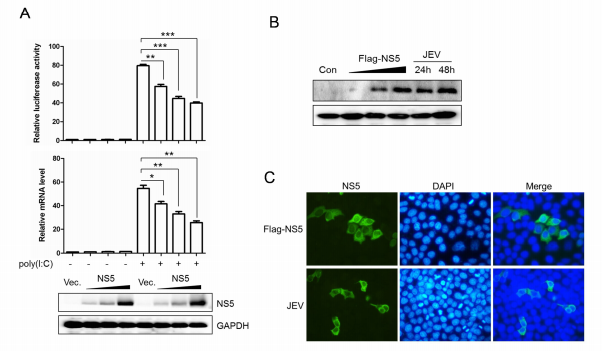
In present study, research fellows from Huazhong Agricultural University and Wuhan Institute of Virology found that Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) NS5 protein could inhibit double strand RNA (dsRNA)-induced IFN-β expression in a dose-dependent manner. Their data further demonstrated that JEV NS5 suppressed the activation of IFN transcriptional factors, IRF3 and NF-κB. However, there was no defect in the phosphorylation of IRF3 and degradation of IκB, an upstream inhibitor of NF-κB, upon NS5 expression, indicating a direct inhibition of the nuclear localization of IRF3 and NF-κB by NS5. Mechanically, NS5 was shown to interact with the nuclear transport proteins, KPNA2, KPNA3 and KPNA4, which competitively blocked the interaction of KPNA3 and KPNA4 with their cargo molecules, IRF3 and p65, a subunit of NF-κB, and thus inhibited the nuclear translocation of IRF3 and NF-κB. Furthermore, overexpression of KPNA3 and KPNA4 restored the activity of IRF3 and NF-κB and increased the production of IFN-β in NS5-expressing or JEV-infected cells. Additionally, an up-regulated replication level of JEV was shown upon KPNA3 or KPNA4 overexpression. These results suggest that JEV NS5 inhibits the induction of type I IFN by targeting KPNA3 and KPNA4.
Link: http://jvi.asm.org/content/early/2017/02/02/JVI.00039-17.long
ZHANG Bo
E-mail: zhangbo@wh.iov.cn
Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, Hubei, People's Republic of China(http://english.whiov.cas.cn/)